By Rebecca Martin and Marissa Marvelli
This evening members of the City of Kingston Planning Board, Historic Landmarks Preservation Commission (HLPC), and the Heritage Area Commission (HAC) will convene for a joint meeting to discuss the visual impact analysis and other architectural drawings that were prepared for the proposed Kingstonian development by the applicant’s architect. It is one of nine consultant reports submitted in July as part of the project’s State Environmental Quality Review (SEQR). These reports are meant to help inform the Planning Board, the lead agency, as it completes Parts 2 and 3 of the Environmental Assessment Form (EAF), which assesses a project’s potential impacts, including those on historic, archaeological, architectural, or aesthetic resources. Although the applicant’s attorney volunteered to fill out the forms during the last Planning Board meeting on September 11th, completing these forms is the responsibility of the lead agency; the applicant cannot be its own critic.
Marissa Marvelli, a historic preservation consultant and a former member of the HLPC, has prepared an illustrated guide for evaluating new construction in the Stockade Historic District. It is meant to complement the questions asked in the EAF Part 2. While her guide does not attempt to prescribe design solutions as that is the responsibility of the project’s architect, it does call attention to the special qualities, features, and significance of the district. The guide is viewable at the bottom of this post.
Understanding Impacts on Historic, Archaeological, Architectural, and Aesthetic Resources
The following questions come directly from the NYS Department of Environmental Conservation’s SEQR Workbook, which is meant to assist the lead agency in completing a Part 2 EAF. They pertain specifically to impacts on historic, archaeological, architectural, and/or aesthetic resources:
- Does the proposed project contain, or does it adjoin a structure listed on the national or state register of historic places, or a structure that has been determined by the Commissioner of OPRHP to be eligible for listing on the State Register of Historic Places? (The Kingstonian project site does not contain such a structure.)
- Is the proposed project located in a national, state, or local historic district, or one that has been determined by the Commissioner of OPRHP to be eligible for listing on the State Register of Historic Places? (The Stockade Historic District is a designated local district. It is also listed on the National and State Registers.)
- Does the community have a local survey, inventory, or list of important historic, architectural, or aesthetic resources, and are there any resources recorded on or near the project site? (Yes, the Senate House & Grounds to name one important one.)
- Is the proposed project located in an archaeologically sensitive area? (Yes.)
- If the project site is located in such an area, additional information may need to be collected to see if there are any resources in or near the specific location that may be impacted.
- Are there historic or archaeological resources on the property or nearby?
- Has an archeological survey been done to confirm if the project site has any such resources? (Only a Phase 1a survey has been completed so far. Consulting archaeologist Joseph Diamond has recommended a Phase 1b.)
- Will the proposed project directly or indirectly affect them? How? (A Phase 1b survey would reveal potential impacts.)
- Is the proposed project located in a scenic overlay district, scenic byway, or scenic area of state significance? (No.)
- Is there a specific architectural style that identifies the community or neighborhood? For example, most buildings may be predominantly of colonial architecture, or perhaps all the buildings in the neighborhood are constructed of red brick. (Yes, the immediate blocks are predominantly 19th-century brick commercial buildings. The district boasts the largest assemblage of 18th and early 19th century stone buildings in New York.)
- Will the project block important scenic views, or change the aesthetic character of an area? (Yes, the project’s scale and massing break drastically with the pattern of the district and the development would close a historic street to create an open plaza, which has no precedent in the district. It also proposes to drastically alter the topography, which is important to the district’s history and significance.)

Measuring Impacts
According to the EAF Part 2 Workbook, in considering impacts, the agency must decide if that impact will be small or moderate to large. This decision should be based on the magnitude of the potential impact. Magnitude is not just the physical size of the project in feet or acres. Magnitude also considers the scale and context of a proposed project, and severity of that project’s impact. The Workbook gives guidance on assessing impact according to each environmental topic, including historic and archaeological resources.
A small impact could occur if:
- There is no historic or archaeological resource on the site, but there may be a small impact to community character because of concerns over consistency with existing architectural and aesthetic resources.
- There are historic or archaeological resources on the site, but the project design is such that no disturbances or major changes to historic structures will occur. For example, the location where archaeological resources exist will be avoided, or the historic structure on the property will be maintained and restored.
- Minor disturbances to the resources will occur or minor changes to the aesthetic or scenic quality of the area but these do not destroy the historic resource or drastically change the character of the area.
- Work at a location that is locally designated and historic preservation permits are issued that indicate identified work as being in compliance with relevant local historic preservation code.
Moderate to large impacts may occur if:
- Historic structures are planned to be demolished or relocated as part of the development plan.
- Historic structures are to be remodeled in a way that destroys or damages its historic value.
- The project introduces an architectural design that is not consistent with a designated historic district, or a district that has been determined eligible for listing on the State Register, and that is not consistent with the long-term vision the community has for its aesthetic character as identified in an adopted comprehensive plan.
- The project changes the character or view of important aesthetic resources.
SHPO Believes Project Will Have ‘Adverse Effects’ on the Historic District
In a September 19th letter to the Kingstonian applicant, the State Historic Preservation Office (SHPO) provided its comments on the project after its review of the materials. The comments are part of a consultation mandated by Section 14.09 of the New York Parks, Recreation and Historic Preservation Law. It is required for projects that are funded, licensed or approved by state or federal agencies.
The letter describes the agency’s concerns:
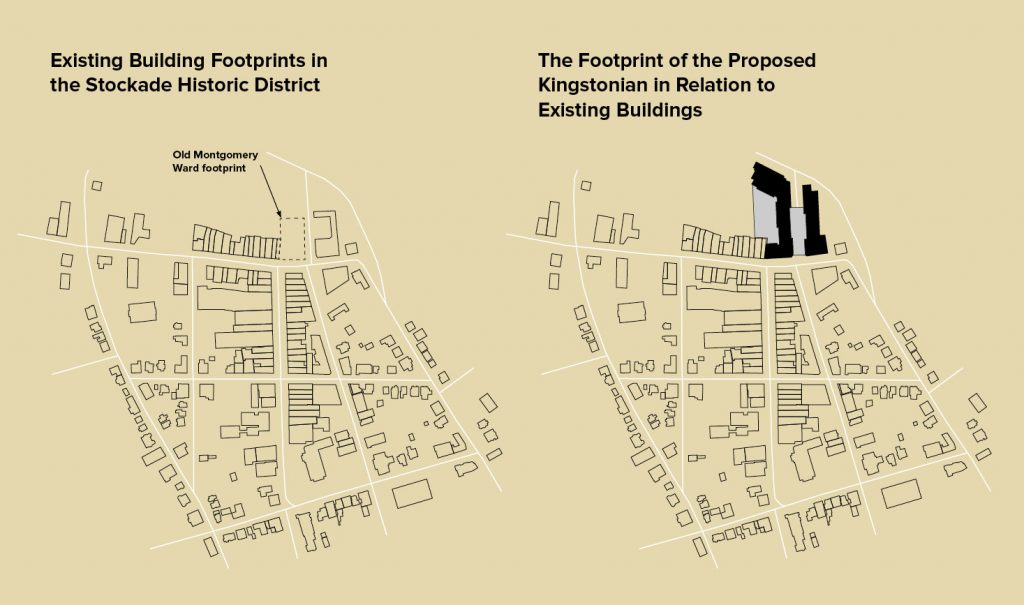
- North Front Street is the traditional district boundary marked by a distinct natural drop-off down toward the Esopus Creek. This natural contour clearly marks the northern boundary of the historic 1658 stockade. The lower portion to the north of the district now contains modern buildings and the shopping plaza further to the north, but the historic boundary remains readily apparent and continues to characterize the district. The new construction would significantly alter the northern district boundary and would be clearly visible from within the historic district. The Montgomery Ward building, now demolished, was the only structure that extended significantly beyond that traditional northern border. The proposed new development is much larger and would extend well beyond the old Montgomery Ward footprint.
- By the mid-19th century, when the commercial street front was developed, the section of Fair Street extending north from North Front Street was established to access railroad facilities and the lumber yards. This historic street, which allows pedestrian and vehicular access to the district, would be virtually eliminated as part of the proposed development.
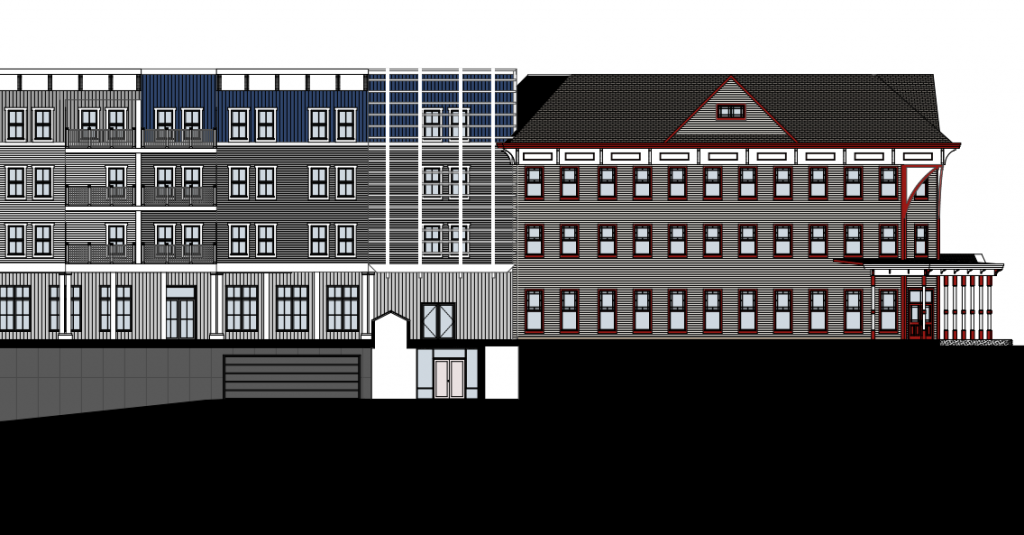
- The historic commercial and residential buildings of the Kingston Stockade are characterized by a variety of materials, styles, and colors. The new construction is monolithic compared with the surrounding district. Though the currently proposed design attempts to reference the historic setting and surrounding architecture, we believe that a much greater effort is warranted for a construction of this scale.
SHPO’s comments provided under Section 14.09 are not advisory. The applicant must consult with agency staff to find acceptable solutions for avoiding, mitigating, or minimizing any adverse effects identified.
Confusion About the Boundaries of the Stockade Historic District
According to citizens who were present, during a presentation of the Kingstonian to the HLPC at its September 5th meeting, questions were raised about the location of the northern boundary of the Stockade Historic District as it pertains to their project site. The Kingstonian project team has apparently been operating under the assumption that the boundary bisects the northern part of the City-owned parcel because that is what is shown on SHPO’s Cultural Resource Information System, which maps of State and National Register properties and districts throughout the state. Because the HLPC’s review of a project ends at the boundary line, it would be to the applicant’s advantage to have the boundaries more constricted.
The boundaries of the State and National Register historic district are not relevant to the HLPC because the HLPC reviews only locally-designated districts and landmarks. The boundaries of local districts are approved by the Common Council and are included in the zoning chapter of the City’s Administrative Code. It is clear that the local historic district boundaries avoid bisecting any parcels. Curiously, the applicant is not questioning the boundaries of the Stockade Mixed-Use Overlay District, which mirror those of the local historic district and is of great worth to this project.